Socket Weld Coupling
Socket Weld Coupling Manufacturer & Supplier
A Socket Weld Coupling is a sort of pipe fitting that connects two pipes or a pipe to another fitting in a piping system. It forms a strong, leak-proof connection suitable for high-pressure, high-temperature applications. The coupling has a recessed section (socket) into which the pipe is fitted and fillet welded around the outside surface.


| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Socket Weld Coupling (Forged Socket Weld Full or Half Coupling) |
| Function | Connects two pipes end-to-end to extend a pipeline or join pipes of the same or different diameters (full coupling) or cap a pipe end (half coupling). |
| Types | – Full Coupling: Connects two pipes of the same or different diameters. – Half Coupling: Connects one pipe or caps a pipe end. – Reducing Coupling: Connects pipes of different diameters. |
| Size Range | 1/8″ to 4″ (DN6 to DN100) |
| Pressure Rating | Class 3000, 6000, 9000 (suitable for high-pressure applications). |
| Standards | ASME B16.11, BS3799, MSS SP-83, GB/T 14383 |
| Materials | – Stainless Steel: ASTM A182 F304, F304L, F316, F316L, F310, F321, F347, F904L – Carbon Steel: ASTM A105, A350 LF2 – Alloy Steel: ASTM A182, A335, A234 (P1, P5, P9, P11, P22, P91) – Nickel Alloys: Inconel, Monel, Hastelloy (e.g., UNS 2200, 4400, 10276) – Duplex/Super Duplex Steel: ASTM A182 F51, F53, F55 – Copper Alloys: ASTM SB 111, SB 466 (C 70600, C 71500) – Others: Galvanized, Brass, Mild Steel, Titanium |
| Socket Weld Cross Section | Features a recessed socket for pipe insertion with a 1/16″ (1.6 mm) expansion gap to accommodate thermal expansion and prevent stress. |
| Applications | – Small-bore, high-pressure piping systems (e.g., oil and gas, chemical plants, power generation, fire sprinkler systems). – Conveying flammable, toxic, or expensive materials where leakage is critical. – Steam systems (300–600 PSI). |
| Connection Type | Socket Weld (fillet-type seal welds); can have mixed connections (e.g., socket weld one end, threaded the other). |
| Key Features | – High leakage integrity and structural strength. – Simple fit-up, no beveling required, reducing construction costs compared to butt-weld fittings. – Permanent connections with good flow characteristics. – Not suitable for highly corrosive or radioactive applications due to potential corrosion in the expansion gap. |
| Dimensional Tolerances | – Socket Bore (B): Max/min dimensions per ASME B16.11. – Bore Diameter (D): Max/min dimensions. – Socket Wall Thickness (C): Average thickness, with minimum at partial areas. – Center to Bottom of Socket (A): ±1.5 mm (NPS 1/2–3/4), ±2 mm (NPS 1–2), ±2.5 mm (NPS 2.5–4). – Depth of Socket (J): Minimum 9.5 mm. |
| Limitations | – Potential for stress due to thermal expansion in the socket gap. – Not ideal for hydrogen service or highly corrosive environments. – Limited to small-bore piping (NPS 2 or smaller). |
| Marking and Packaging | – Marked with alloy name, outside diameter, wall thickness, pressure class, and heat number. – Packaged in plastic bags, cartons, or seaworthy wooden cases/pallets for safe transportation. |
| Manufacturers/Suppliers | Available from suppliers like Marcel Piping, Skyland Metal, Kamlesh Metal, Teshi Group, and others, with exports to over 50 countries. |
Socket Weld Coupling Dimensions
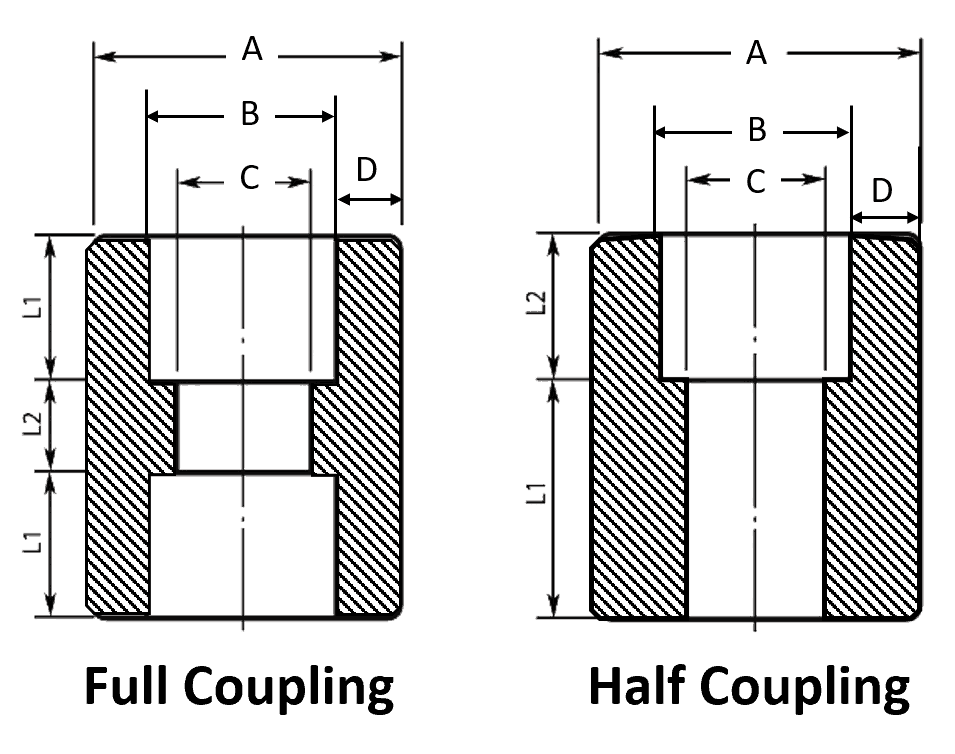
| NOMINAL PIPE SIZE | OUTER DIAMETER | SOCKET BORE DIAMETER | BORE DIAMETER OF FITTINGS | BORE DIAMETER OF FITTINGS | BORE DIAMETER OF FITTINGS | WALL THICKNESS # 3000 | WALL THICKNESS # 3000 | WALL THICKNESS # 6000 | WALL THICKNESS # 6000 | WALL THICKNESS # 9000 | WALL THICKNESS # 9000 | FULL COUPLING | FULL COUPLING | HALF COUPLING | HALF COUPLING |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inch. | A | B | C – 3000 | C – 6000 | C – 9000 | D | D | D | D | D | D | L1 | L2 | L1 | L2 |
| Maximum Minimum | Maximum Minimum | Maximum Minimum | Maximum Minimum | Average | Minimum | Average | Minimum | Average | Minimum | ||||||
| 1/8 | B+D | 11.2 10.8 | 7.6 6.1 | 4.8 3.2 | 3.18 | 3.18 | 3.96 | 3.43 | 9.5 | 6.5 | 9.5 | 16.0 | |||
| 1/4 | B+D | 14.6 14.2 | 10.0 8.5 | 7.1 5.6 | 3.78 | 3.30 | 4.6 | 4.01 | 9.5 | 6.5 | 9.5 | 16.0 | |||
| 3/8 | B+D | 18.0 17.6 | 13.3 11.8 | 9.9 8.4 | 4.01 | 3.50 | 5.03 | 4.37 | 9.5 | 6.5 | 9.5 | 17.5 | |||
| 1/2 | B+D | 22.2 21.8 | 16.6 15.0 | 12.5 11.0 | 7.2 5.6 | 4.67 | 4.09 | 5.97 | 5.18 | 9.35 | 8.18 | 9.5 | 9.5 | 9.5 | 22.5 |
| 3/4 | B+D | 27.6 27.2 | 21.7 20.2 | 16.3 14.8 | 11.8 10.3 | 4.90 | 4.27 | 6.96 | 6.04 | 9.78 | 8.56 | 12.5 | 9.5 | 12.5 | 24.0 |
| 1 | B+D | 34.3 33.9 | 27.4 25.9 | 21.5 19.9 | 16.0 14.4 | 5.69 | 4.98 | 7.92 | 6.93 | 11.38 | 9.96 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 28.5 |
| 1 1/4 | B+D | 43.1 42.7 | 35.8 34.3 | 30.2 28.7 | 23.5 22.0 | 6.07 | 5.28 | 7.92 | 6.93 | 12.14 | 10.62 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 30.0 |
| 1 1/2 | B+D | 49.2 48.8 | 41.6 40.1 | 34.7 33.2 | 28.7 27.2 | 6.35 | 5.54 | 8.92 | 7.8 | 12.7 | 11.12 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 32.0 |
| 2 | B+D | 61.7 61.2 | 53.3 51.7 | 43.6 42.1 | 38.9 37.4 | 6.93 | 6.04 | 10.92 | 9.5 | 13.84 | 12.12 | 16.0 | 19.0 | 16.0 | 41.0 |
| 2 1/2 | B+D | 74.4 73.9 | 64.2 61.2 | 8.76 | 7.67 | 16.0 | 19.0 | 16.0 | 43.0 | ||||||
| 3 | B+D | 90.3 89.8 | 79.4 76.4 | 9.52 | 8.30 | 16.0 | 19.0 | 16.0 | 44.5 | ||||||
| 4 | B+D | 103.8 100.7 | 103.8 100.7 | 10.69 | 9.35 | 16.0 | 19.0 | 16.0 | 48.0 | ||||||
| All Dimensions are in mm | |||||||||||||||
Types of Socket Weld Coupling:
Full Coupling
Used to connect two pipes or a pipe to a fitting of the same diameter.
Half Coupling
Used for branching from a large pipe to a smaller one.
Reducing Coupling
Connects pipes of different diameters.
Available Classes:
Class 3000
Class 6000
Class 9000
Advantages:
Excellent strength and leakage integrity
Ideal for small diameter, high-pressure piping
Easy to install and align
Applications:
Oil & gas pipelines
Petrochemical industries
Steam systems
Power plants
High-pressure fluid conveyance
